Prosthetics ( penile prosthesis and testicular implant)
Penile Prosthesis
Penile implants are devices placed inside the penis to allow men with erectile dysfunction (ED) to get an erection. Penile implants are typically recommended after other treatments for ED fail.
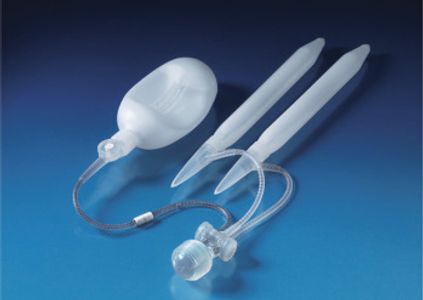
There are two main types of penile implants, semirigid and inflatable. Each type of penile implant works differently and has various pros and cons.
The placement of penile implants requires surgery. Before choosing penile implants, make sure you understand what surgery involves, including possible risks, complications and follow-up care.
Why it's done
For most men, erectile dysfunction can be successfully treated with medications or use of a penis pump (vacuum constriction device). You might consider penile implants if you aren't a candidate for other treatments or you can't get an erection sufficient for sexual activity by using other methods.
Penile implants can also be used to treat severe cases of a condition that causes scarring inside the penis, leading to curved, painful erections (Peyronie's disease).
Penile implants aren't for everyone. Your doctor might caution against penile implants if you have:
- ED that's situational, the result of a relationship conflict or potentially reversible
- An infection, such as a pulmonary infection or urinary tract infection
- Diabetes that isn't well-controlled
Keep in mind that while penile implants allow men to get an erection, they don't increase sexual desire or sensation. Most penile implants also won't make your penis any larger than it naturally is at the time of surgery. In fact, your erect penis might be slightly shorter than it used to be.
Risks
Risks of penile implant surgery include:
- Infection. As with any surgery, infection is possible. You might be at an increased risk of infection if you have a spinal cord injury or diabetes.
- Implant problems. New penile implant designs are reliable, but in rare cases the implants might malfunction. Surgery is necessary to remove, repair or replace a broken implant.
- Internal erosion or adhesion. In some cases, an implant might stick to the skin inside the penis or wear away the skin from inside the penis. Rarely, an implant breaks through the skin. These problems are sometimes linked to an infection.
Treating an infection
Infections after penile implant surgery typically occur in the first few weeks or possibly years later. Early infections can cause swelling of the scrotum, pus buildup and fever. Later infections might involve persistent or recurrent long-term pain.
Surgery to remove the implant is likely necessary to treat an infection. Replacing a penile implant can be complicated and can lead to a buildup of scar tissue and a decrease in penis length.
How you prepare
Initially, you'll talk to your doctor or a urologist about penile implants. During your visit, your doctor will likely:
- Review your medical history. Be prepared to answer questions about current and past medical conditions, especially your experience with ED. Talk about any medications you're taking or have taken recently, as well as any surgeries you've had.
- Do a physical exam. To make sure penile implants are the best options for you, your doctor will do a physical exam, including a complete urologic exam. Your doctor will confirm the presence and nature of ED, and make sure that your ED can't be treated in another way.
He or she will also try to determine whether there's any reason that penile implant surgery is likely to cause complications. Your doctor will also examine your ability to use your hands, since some penile implants require greater manual dexterity than others.
- Discuss your expectations. Make sure you understand what the procedure involves and the type of penile implant that suits you best. It's also important to know that the procedure is considered permanent and irreversible.
Your doctor will also explain the benefits and risks, including potential complications. Ideally, you'll include your partner in the discussion with your doctor.
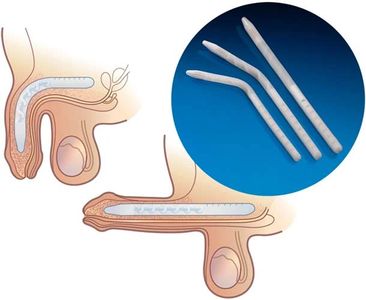
Types of penile implants
There are two main types of penile implants:
- Inflatable implants. Inflatable devices, the most common type of penile implant used, can be inflated to create an erection and deflated at other times. Three-piece inflatable implants use a fluid-filled reservoir implanted under the abdominal wall, a pump and a release valve placed inside the scrotum, and two inflatable cylinders inside the penis. To achieve an erection, you pump the fluid from the reservoir into the cylinders. Afterward, you release the valve inside the scrotum to drain the fluid back into the reservoir. The two-piece model works in a similar way, but the fluid reservoir is part of the pump implanted in the scrotum.
- Semirigid rods. Semirigid devices are always firm. The penis can be bent away from the body for sexual activity and toward the body for concealment. A positionable penile implant is a semirigid device with a central series of segments held together with a spring on each end. It can maintain upward and downward positions better than other semirigid rods can.
Other special designs can fit a shortened penis, or one that's larger than average. Some inflatable penile implants are also available with antibiotic coatings, which might help reduce the risk of infection.
Comparing implant types
When choosing which type of penile implant is right for you, consider your personal preference and your medical history. Your doctor might suggest one type of design over another based on your age, risk of infection, and health conditions, injuries or medical treatments you've had in the past.
Type of penile implant
Three-piece inflatable
pros
- Creates the most natural, rigid erection
- Provides flaccidity when deflated
cons
- Has more parts that could malfunction than does any other implant
- Requires a reservoir inside the abdomen
Two-piece inflatable
pros
- Provides flaccidity when deflated
cons
- Is mechanically more complicated than is a semirigid implant
- Provides less firm erections than does a three-piece implant
Semirigid rod
pros
- Has a low chance of malfunction due to the small number of parts
- Is easy to use for those with limited mental or manual dexterity
cons
- Results in a penis that is always slightly rigid
- Puts constant pressure on the inside of the penis, which can cause injury
- Can be difficult to conceal under clothing
Before penile implant surgery you might also need to:
- Avoid certain medications. Your doctor might recommend that you temporarily stop taking aspirin and anti-inflammatory drugs, which can increase your risk of bleeding.
- Arrange for a ride home. Ask your doctor when you'll be able to go home after surgery. Penile implant surgery typically involves an overnight stay.
- Limit food and liquids. Don't eat or drink anything after midnight before your surgery, or follow specific instructions from your doctor.
What you can expect
Before the procedure
Penile implant surgery is usually done at a surgery center or hospital. Your doctor might give you medication to make you unconscious during the surgery (general anesthesia) or medication that blocks pain in the lower part of your body (spinal anesthesia).Your doctor will give you IV antibiotics to help prevent infection. The surgery site will also be shaved immediately before surgery to reduce the risk of infection.
During surgery
A tube (catheter) might be inserted into your bladder via your penis to collect urine at some point during surgery. Your surgeon will make an incision below the head of the penis, at the base of the penis or in the lower abdomen.Next, your surgeon will stretch the spongy tissue in the penis that would normally fill with blood during an erection. This tissue is inside each of the two hollow chambers called the corpora cavernosa.Your surgeon will choose the correct size implant and place the implant cylinders inside your penis. All sizes are customized to your exact body measurements.If your doctor is implanting a two-piece inflatable device, a pump and valve are placed inside the scrotum. For a three-piece device, your doctor will also implant a fluid reservoir under the abdominal wall through an internal incision.Once the device is in place, your surgeon will sew the incisions closed. Penile implant surgery usually takes 45 minutes to an hour.
After surgery
After penile implant surgery, you'll likely need to take medications to ease pain. Mild pain might persist for several weeks. You might also need to take antibiotics for one week to prevent infection.Your doctor might recommend keeping your penis up on your lower abdomen and pointing toward your bellybutton during the healing process to prevent downward curvature.Your doctor will provide specific instructions about when you can resume normal activities. Most men can resume strenuous physical activity and sexual activity about four to six weeks after surgery. You'll likely need to return to your doctor to have your stitches removed in about two weeks.At this point, your doctor might recommend fully inflating and deflating inflatable penile implants twice a day to give you practice using them and stretch the area surrounding the cylinders.
Results
Although penile implants are the most invasive and least often chosen treatment for erectile dysfunction, most men and their partners report satisfaction with the devices. The 10-year device survival is between 60 and 80 percent.
Testicular Prosthesis
When a male is born without a testicle or must have one removed due to injury or disease, a testicular prosthesis may be used.

What is a testicular prosthesis?
A prosthesis is any artificial device used to replace a body part. When a male is born without a testicle or must have one removed due to injury or disease, a doctor may implant a testicular prosthesis to fill in the empty space in the scrotum (the sac that contains the testicles). The prosthesis is used only to improve appearance and to calm psychological fears. It does not have any functions of a real testicle. More often than not, requests for a testicular prosthesis come from those who are born with and later lose a testicle, rather than from those who have always been missing a testicle.
Testicular prostheses have been in use since the 1940s. In the past they were made of a variety of materials. Now, however, they are mainly made of silicone rubber filled with either silicone gel or saline (salt water). A testicular prosthesis will have the weight, shape, and feel of a normal testicle and will be available in different sizes so that a good match is made to the patient’s body.
About

What conditions or events can cause a missing testicle?
- Malformed or missing at birth
- Surgical removal due to injury, such as severe torsion (twisting)
- Failure to descend into the scrotum
- Removal due to infection
- Removal in order to treat testicular cancer
- As part of female-to-male gender reassignment surgery
What procedure is used to implant a testicular prosthesis?
- The patient is placed under either general (whole body) anesthesia or local anesthesia that will block sensation in the lower part of the body.
- The surgery may be performed on an outpatient basis or require only a brief stay in the hospital.
- An incision is usually made in the lower part of the groin or scrotum.
- A pouch will be created for the prosthesis.
- The implant is sewn or otherwise fixed into place so that it is in the correct position and will remain there.
- The incision is sewn shut.

Who is at high risk of complications from testicular prosthesis implantation?
Those with the following conditions face a higher risk of complications:
- Diabetics and those with a suppressed immune system, as their chances for infection are increased
- An already existing infection anywhere in the body
- Untreated cancer anywhere in the body
- Previous surgery on the scrotum
What are possible complications of testicular prosthesis implantation surgery?
Known complications of testicular prosthesis insertion include:
- Pain
- Infection
- Hematoma (pooling of blood in the scrotum)
- Dissatisfaction with appearance following surgery
- Scarring around the implant
- Shifting of the prosthesis out of position
- Rupture or leaking of the prosthesis
- The prosthesis being expelled from the body (this usually means that the device is infected)
Checklist for Penile implant surgery
Preoperative
- Cardiology/Medical Clearance
- Urine Culture
- HbgA1c <10
- Stop antiplatelet 5 days prior
Two days prior to surgery
- Oral Antibiotics
- Chlorhexidine gluconate (CHG)4% scrub twice a day
Day of surgery
- Wash with soap and water
- Perioperative antibiotics:
- Hair removal: clippers or razors
- Chlorhexidine scrub prep
